Hands and the structures within them are prone to infections from bacteria, viruses and fungal (microorganisms) sources. The anatomy of the hand is complex in that a relatively trivial injury may cause disproportionate amount of harm.
What types of infection do you get in the hand?
Infections can affect any structure within the hand. Typical infections include those listed below. Click on the picture to find out more about it.
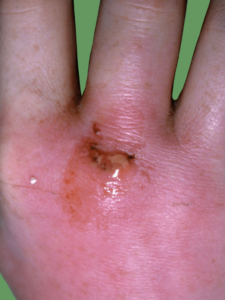
What causes an infection in the hand?
Many infections in the hand can result from a simple cut from a sharp object, including bites from animals. This creates an environment for bugs to enter the wound and spread.
What might increase the risk of infection?
Any patient may get an infection in their hand regardless of any risk factors. However, in patients whose immune system may be compromised, such as in those patients with diabetes, or those being treated taking immunosuppressing medications such as steroids and drugs for rheumatoid arthritis, you may be at risk of a more aggressive infection.
What are the symptoms of a hand infection?
Often patients will present with an area of throbbing pain and redness. The area may be swollen, warm and tender to touch or move. Some finger infections cause the finger to be held in a bent position. There may be evidence of an abscess forming and discharge from a wound. If the infection is more widespread then the patient may have more systemic symptoms such as a fever.
How is an infection diagnosed?
The diagnosis is mainly a clinical one based on the patient’s history and symptoms. Blood tests and tissue swabs may be taken to aid and confirm diagnosis. X-rays may also be taken, more as a screening tool to identify the presence of any bony abnormalities or foreign bodies.